Why Canadian-Made Solar Products Are Superior to Chinese Alternatives: A Look at Regulations and Quality
April 17, 2025As the demand for clean and sustainable energy solutions grows, solar panels have become an increasingly popular choice for homeowners and businesses. While the environmental and energy independence benefits of solar are well-known, understanding the financial aspects of installing solar panels is crucial for making an informed decision. This article explores the costs associated with solar panel installation, potential savings over time, and the government incentives and rebates available to make solar energy more affordable.
Upfront Costs of Installing Solar Panels
The initial investment required for solar panel installation can be a significant concern for many consumers. The overall cost depends on several factors, including the size of the system, the type of solar panels, installation complexity, and geographical location. On average, homeowners in Canada can expect to pay between CAD 15,000 to CAD 25,000 for a fully installed residential solar system that produces enough energy to meet the needs of an average household.
Key Cost Factors:
- System Size: Larger systems that generate more electricity will naturally cost more. The average residential system is typically designed to produce 10,000 to 12,000 kWh annually, which is the average household energy consumption in Canada.
- Panel Type: High-efficiency panels, such as monocrystalline panels, tend to be more expensive than lower-efficiency polycrystalline panels. However, they provide better performance and longer lifespans.
- Installation Costs: The cost of installation can vary based on factors like roof type, location, and the complexity of the installation. Professional installation is required to ensure the system works effectively and meets regulatory requirements.
Potential Savings Over Time
While the initial cost of solar panel installation can be high, the long-term savings can make it a worthwhile investment. The savings primarily come from reducing or eliminating electricity bills, as solar panels allow homeowners to generate their own energy. Other savings factors include:
1. Reduced Energy Bills
- After installation, homeowners can see their monthly electricity bills decrease significantly. Solar systems typically produce a surplus of energy during the day, which can be stored in batteries or fed back into the grid. This reduces reliance on the grid and lowers overall energy expenses.
2. Long-Term ROI
- Solar panels generally have a 25-30 year lifespan, meaning the system will continue to provide free energy for decades after the initial investment. Over time, the savings can far outweigh the installation costs.
- The average payback period for solar panel systems in Canada is between 8 to 12 years, depending on factors like local electricity rates, system size, and available incentives.
3. Increase in Property Value
- Installing solar panels can increase the market value of a home. Studies show that homes with solar installations often sell for 3-4% more than comparable homes without solar, making it an attractive long-term investment.
Government Incentives and Rebates
One of the key factors that make solar panels more affordable is the availability of government incentives and rebates. Both federal and provincial governments in Canada offer various programs to help offset the cost of installation and encourage the adoption of renewable energy. These programs can significantly reduce the upfront costs, making solar panels more accessible to homeowners.
1. Federal Incentives
- The Canada Greener Homes Grant: Homeowners can receive up to CAD 5,000 in grants for energy-efficient upgrades, including solar panel installation. This program is designed to reduce the cost of adopting green technologies and help make homes more energy-efficient.
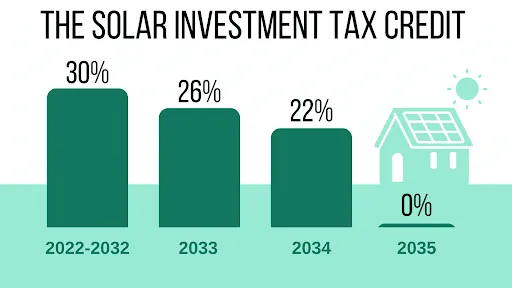
- Investment Tax Credit (ITC): The Canadian government offers a 30% tax credit for solar panel installations, which can be used to offset the cost of purchasing and installing solar systems.
2. Provincial Incentives
- Ontario’s Solar Rebate Program: Ontario offers rebates for homeowners who install solar systems, which can cover a portion of the upfront costs.
- Net Metering: Many provinces, such as Alberta and British Columbia, have net metering programs that allow homeowners to sell excess electricity back to the grid. This can result in credits on electricity bills or even payments, which help offset installation costs.
3. Financing Options
- Many provinces also offer low-interest loans or financing programs to help homeowners afford the upfront cost of solar installation. This allows homeowners to spread the cost over several years while still benefiting from reduced energy bills.
Conclusion
The decision to install solar panels involves significant upfront costs, but the long-term savings, combined with available government incentives, make it an attractive option for many homeowners. Over time, the reduction in energy bills, increased property value, and potential for additional income from net metering can lead to a solid return on investment. With various government rebates and financing options, solar energy has become more accessible, making it a smart choice for homeowners looking to reduce their carbon footprint and energy costs.
While the initial investment can be substantial, the financial benefits of solar power far outweigh the costs, positioning it as a sustainable, cost-effective energy solution for the future.